12 Best Enterprise Patch Management Software

When your company is doing well. The sales are increasing, the teams are working together and it simply works. Then one Tuesday morning, it all comes to a standstill. Your whole network is under ransomware attack. The culprit? An obscure vulnerability in a software application, never updated, that had a small security hole. This is not a scare tactic, this is what happens to thousands of businesses each year.
The silver lining is, it is more possible than you imagine to avoid it. All this is reducible to one thing called patch management.
Consider your smartphone. It periodically requests you to install an update. That update, or patch, will fix bugs, increase performance and most importantly seal security holes that hackers might use. Just take a moment and think what it would be like to be responsible to do that not to one phone, but hundreds or even thousands of computers, servers, and applications within an entire company. It is an enormous undertaking.
best Enterprise Patch Management Software can be used there. It is your secret weapon- an automated system which performs this whole process for you, keeping your business safe, efficient and compliant. This guide will take you through all that you need to know, including what it is and how to select the best platform to fit your organization.
What is the best Enterprise Patch Management Software?
A patch is merely a fix issued by a program developer to fix a certain issue or security vulnerability in their program or operating system. Imagine that it is a virtual Band-Aid. There is a wide variety of software used by companies: Windows, macOS, Microsoft Office, Adobe Acrobat, Slack, Zoom, etc. Every program has its Band-Aids every now and then.
This is the organized cycle that is made to happen by Patch Management:
- Learn what patches exist to each software program within your environment.
- Identify which systems require which patch.
- Apply the patch on a few computers to ensure that it does not break anything.
- Install (or, as it is often called, roll out) the accepted patches on all the concerned computers.
- Confirm that the patches are installed properly and make reports to certify it.
When we take the term Enterprise, we are referring to the execution of this cycle in a large organization. There are desktops, laptops, servers, and remote workers that companies have and that require patching. This work can hardly be done by hand. An IT technician would need to switch between systems (or remotely log into each system), which would consume all his time, be highly prone to errors, and would leave security loopholes.
12 Best Enterprise Patch Management Software
1. Action1
Action1 is a cloud-native enterprise patch management software built on a scalable and secure endpoint management platform. It enables IT teams to automatically discover missing updates and security vulnerabilities, then deploy patches for Windows and widely used third-party applications from a single centralized console. Because the platform is cloud-based, patches can be delivered to both on-network and remote devices without VPNs or on-premise servers, making it well suited for today’s distributed workforces. The platform also includes vulnerability assessment and basic endpoint management capabilities, helping organizations maintain visibility, security, and compliance across all managed systems.
Key Features:
- Supports Windows and third-party application patching.
- Built-in vulnerability discovery and prioritization.
- Cloud-native deployment with no VPN or on-prem infrastructure.
- Automated patch approval and deployment workflows.
- Remote access and basic endpoint management tools.
- Patch status and compliance reporting.
- Best For: Small to mid-size organizations that need reliable, security-focused patch management for remote or hybrid environments.
- Use Case: A growing company uses Action1 to identify vulnerable laptops and automatically deploy critical patches across all employee devices within hours of release.
- Link: https://www.action1.com/patch-management/
2. ManageEngine Patch Manager Plus
Patch Manager Plus by ManageEngine is an best Enterprise Patch Management Software which is employed by many IT professionals because of its extensive coverage and decent support. It is designed as a one-stop patching tool that deals with operating system updates as well as a vast library of third-party software. IT administrators have the granularity they need across the patch management lifecycle, including scanning and detection, testing, and fully automated deployment. The service can be used as a cloud-based solution to support the current dispersed workforces or an on-premise deployment to organizations that prefer to store their data locally.
Key Features:
- Supports windows, macOS, Linux patching.
- Huge library of third-party application patches (more than 850 apps).
- Automated patching by test-and-approve policies.
- Server application patching (e.g. Microsoft Exchange, SQL).
- Compliance and security audit detailed reporting.
- Best For: Small to large businesses requiring a feature rich dedicated patching solution.
- Use Case: A healthcare organization automates the critical security patching of both Windows and special medical software.
- Link: https://www.manageengine.com/patch-management/
3. Automox
Automox is a contemporary cloud-native cyber hygiene platform. It is effective in the modern world of remote employment and makes things easy and offers good automation. The primary objective of the service is to ensure patch management is a breeze. Whether the device is Windows, macOS, or Linux, no matter where it is located, you can see and manage it on a single, intuitive console. Automox relies on more flexible policies and reusable, script-based commands called Worklets that can automate virtually any IT process instead of complex settings. This gives the platform strength to teams that need to go beyond basic patching to total endpoint hardening and configuration, all in a single, quick, convenient cloud-based tool.
Key Features:
- Real cloud-native endpoint management platform.
- Automatic windows, macOS, and Linux patching.
- Custom scripting and task automation using so-called worklets.
- Risk based prioritization and visibility of vulnerability.
- Policy based management.
- Best For: Modern enterprises (of any scale) with remote or hybrid workforces.
- Use Case: A rapidly expanding tech company that has employees worldwide uses Automox to automatically patch and secure all company laptops within 24 hours of the announcement of any critical vulnerability.
- Link: https://www.automox.com/
4. Scalefusion
Scalefusion UEM solution that includes patch management capability for modern enterprises. It is built for IT teams that want tighter control over OS and application updates without adding operational complexity. Scalefusion approaches patching as part of overall endpoint health, combining visibility, policy-driven updates and reporting from a single dashboard. It includes third-party application patching, helping organizations reduce exposure from commonly targeted software. With flexible scheduling, reboot controls, rollback support and audit-ready reports, Scalefusion fits well in environments that value compliant and predictable patch behavior.
Key Features:
- OS patch management for Windows, macOS and Linux endpoints.
- Third-party application patching for commonly used apps like browsers and collaboration tools.
- Policy-based patch controls including active hours, deferrals and reboot behavior.
- Real-time visibility into patch status: pending, installed, failed or rolled back.
- Patch rollback to quickly restore stability if an update causes issues.
- Detailed reporting with patch history, compliance views and exportable audit logs.
- Best For: Mid-sized to large organizations looking for patch management as part of a broader endpoint management and compliance strategy.
- Use Case: A distributed enterprise with Windows laptops, macOS devices and Linux systems uses Scalefusion to keep OS and third-party applications updated during off-hours. Track compliance centrally and quickly roll back problematic updates without disrupting end users.
- Link: https://scalefusion.com/automated-patch-management-software
5. NinjaOne
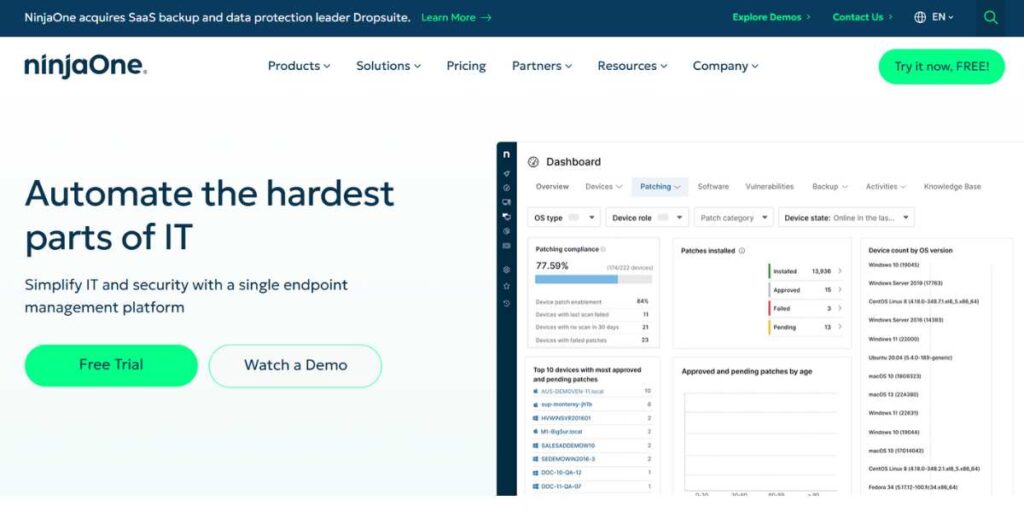
NinjaOne is a Managed Service Provider (MSP) and internal IT department-focused unified IT operations platform. As a leading enterprise patch management software, patch management is central to its wider portfolio that also includes remote monitoring and management (RMM), endpoint security, backup, and others. Its greatest strength is the unified design; you are not getting just a patching tool, you are getting a complete picture of the health of an endpoint. The interface is celebrated as lightning-fast, simple and modern and reduces training time and makes routine operations fun. It has a robust and highly automated patch engine that allows you to have fine-grained control over the updates of the OS and third-party apps on Windows and macOS computers through a single pane of glass you go to do all other IT tasks.
Key Features:
- Components of an all-in-one RMM platform (monitoring, management, patching)
- Rapid, modern, and intuitive user interface
- Very automated patching in Windows and macOS
- Fine-grained control over patch scanning, approval
- Scheduling Remote access and management tools built-in
- Best For: Managed Service Providers (MSPs) and small-to-mid-size business (SMB) IT departments
- Use Case: An MSP uses NinjaOne to patch 50 small business customers and has created different patch policies.
- Link: https://www.ninjaone.com/
6. Atera
Another all-in-one platform that is developed with managed service providers and IT professionals in mind is Atera. As a robust enterprise patch management software, its greatest attraction is a per-technician pricing system that is highly appealing to the emerging companies. Similar to NinjaOne, patch management is highly incorporated into Atera Remote Monitoring and Management (RMM) and Professional Services Automation (PSA) packages. This implies that you will be able to patch, support tickets and even bill your time all in the same ecosystem. The philosophy of Atera is based on efficiency and cost effectiveness. It offers strong automation to find, approve and install Windows, Mac, and software patches. It is also strong in bringing the advanced capabilities to the fore to be affordable and available to even the small IT teams in order to use the powerful profiles of automation.
Key Features:
- System of RMM and PSA in one.
- Per-technician disruptive pricing model.
- Highly automated OS and third-party application patching.
- Built in helpdesk, billing and reporting.
- Large scripting support of custom tasks.
- Best For: MSPs and budget-minded internal IT departments.
- Use Case: An IT consultant works as a freelancer with a number of small businesses under a single- technician Atera license and deploys patches to all their clients automatically.
- Link: https://www.atera.com/
7. Ivanti Neurons for Patch Management
Ivanti has been a powerhouse in enterprise IT management over the years, and it reflects in its patch management tool. As a trusted enterprise patch management software, Ivanti Neurons for Patch Management is an enterprise-level, scalable platform characterized by its extensive collection of third-party patches—frequently referred to as one of the most extensive in the market. Ivanti has a new, AI-powered platform called Neurons, which is aimed at enabling organizations to self-heal and self-secure. It applies AI to offer risk-based prioritization, forecasting which patches are likely to be weaponized by attackers, and assisting you to repair those first. It provides patching independence, with already tested content, which greatly minimizes the chances of a poor patch leading to an outage. It is a strong, mature, and powerful solution designed to work in complex, large-scale environments.
Key Features:
- Third-party application patch catalog leading in the market.
- Risk prioritization and patch reliability powered by AI.
- Pre-deployment testing of autonomous patching.
- Windows, macOS, Linux, and virtual system support.
- Close interface with other Ivanti security and IT management products.
- Best For: Large companies and organizations that have complicated, multi-faceted IT environments.
- Use Case: A large financial institution that has thousands of endpoints and has compliance requirements works with Ivanti Neurons to prioritize vulnerabilities.
- Link: https://www.ivanti.com/products/ivanti-neurons-for-patch-management
8. JumpCloud
JumpCloud is not like that. It is a complete Open Directory Platform™ that is supposed to contain all the truth about users, identities, and devices used by them. While not a traditional enterprise patch management software, patch management is an exception in this broader context. The aim of the platform is to consolidate a chaotic pile of IT tools, such as Active Directory, single sign-on (SSO), mobile device management (MDM), and transform them into a single cloud-based solution. Using it, you can impose Windows, macOS, and Linux updates on your entire fleet directly through the same console that you use to control user access. The connection of security policy and user and device identity is strong. Although JumpCloud cannot compete with a specialized solution such as Patch Manager Plus in terms of depth, its true power is in this close, all-in-one integration, and it is an ideal choice for organizations that are looking to upgrade their entire IT and identity infrastructure.
Key Features:
- A component of an end-to-end directory, identity and device management system.
- Windows, macOS, and Linux Patching as a Cloud service.
- Controls that are policy-based to mandate update schedules.
- Combines patching and user identity and security commands.
- Control access, SSO, MFA, and devices centrally.
- Best For: Cloud-first organizations that would like to harmonize their IT stack and centralize device and user management.
- Use Case: A contemporary SaaS organization that does not have a traditional server-room deploys JumpCloud to control employee access to applications.
- Link: https://jumpcloud.com/
9. Microsoft Intune
One of the key components of Microsoft Endpoint Manager is called Intune. Being a cloud-based platform, it assists organizations in managing their devices and applications at a single location. Intune is the logical choice of companies that already use Microsoft 365 and Azure. Intune is able to manage Windows Update by directing Windows devices using Windows Updates. This allows administrators to establish stringent policies on the cloud and only send updates to the devices that comply with the policies. The platform verifies the compliance and prevents the access of non-compliant devices to corporate resources. Although Intune is yet to have native patching capabilities on third-party software, its close integration with Windows and such tools as Microsoft Defender for Endpoint makes it an excellent choice in Microsoft-focused companies.
Key Features:
- Windows Update for Business native integration.
- Policy-based Update rings to deploy in phases and control.
- Cloud management of Windows, macOS, iOS, and Android.
- conditional access policy enforcement and device compliance.
- Risk-based vulnerability management with integration with Microsoft Defender.
- Best For: Businesses that are invested in the Microsoft 365 and Azure cloud stack.
- Use Case: A large enterprise Intune requires all laptops used in the firm install essential Windows security updates within 7 days of release, automatically locking out non-compliant laptops to SharePoint and Exchange Online.
- Link: https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/security/business/endpoint-management/microsoft-intune
10. Kaseya VSA
Kaseya VSA is an RMM tool that has been in operation over ten years. It assists managed service providers (MSPs) and internal IT departments in keeping large, complex IT systems in check. VSA has patch management integrated into it. The mature automation engine is the strongest point of the platform because it allows technicians to develop multi-step scripts and policies to perform virtually any IT procedure, including sophisticated patching schedules. It has complete support of Windows and macOS operating systems and a broad catalogue of well-known third-party applications so that technicians can manage thousands of endpoints through a single management console.
Key Features:
- Policy-based management engine and advanced automation.
- Automated patching of operating systems (Windows, macOS) and third-party software.
- IT asset discovery, auditing and management.
- Incorporated with a complete set of IT services (backup, security, PSA).
- Wide coverage of patch status, history and compliance.
- Best For: VSA is most appropriate to existing MSPs and large corporate IT departments who deal with complex environments.
- Use Case: A common scenario would be an MSP utilizing VSA to maintain the IT infrastructure of a chain of retail stores, which automatically deploys overnight patches to Windows.
- Link: https://www.kaseya.com/products/vsa/
11. Syxsense
Syxsense is an integrated endpoint security and management platform that removes the gaps that are created by using multiple IT and security tools. It integrates vulnerability scanning, patch management and remediation in a single automated process. IT teams, with Syxsense, can view missing OS and third-party patches, identify other security risks, including open ports or software misconfigurations, and remediate them all through a single console. It also contains a robust visual workflow designer, Syxsense Cortex 10, which enables administrators to create complex automation chains with a drag-and-drop interface, so that remediation is quick and repeatable on Windows, macOS, and Linux machines.
Key Features:
- Unified scanning, patching and security remediation platform.
- Autopatching of Windows, macOS, and Linux.
- Endpoint querying and management in real time.
- Drag-and-drop automation engine (Syxsense Cortex 1).
- Live dashboards on security posture, vulnerability and patch compliance.
- Best For: Security-minded organizations that desire to have vulnerability management and patching in a single solution.
- Use Case: A university security team uses Syxsense to scan all of the computer labs on campus to identify vulnerabilities.
- Link: https://www.syxsense.com/
12. ConnectWise Automate

ConnectWise Automate is a strong RMM tool, and it is the heart of the ConnectWise ecosystem. It was constructed primarily with Technology Solution Providers (TSPs) and MSPs. Automate is special due to its depth, flexibility and automation. Its patch management is good; it allows technicians to monitor every patch cycle: scanning, approval policies, deployment, and in-depth reports. The primary strength of Automate is a powerful scripting engine. Using this engine, technicians are able to write and execute highly customized scripts to virtually any IT task they require.
Key Features:
- Scripting engine, industry leading, powerful and flexible automation.
- Control of Windows OS and third party application patching.
- Self-healing proactive device monitoring.
- Integration with the ConnectWise suite (PSA, Control, etc.) on a deep level.
- Deployment is to be accelerated by out-of-the-box monitoring and automation.
- Best For: MSPs and IT service providers who need extensive customization and automation muscle.
- Use Case: A large MSP has ConnectWise Automate execute a custom pre-patching script that backs up a client-critical database server.
- Link: https://www.connectwise.com/platform/unified-management/automate
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
It is thrilling to introduce a new best Enterprise Patch Management Software but it is easy to go wrong. Be careful of these pitfalls:
- Forgetting to Test Patches: It is tempting to send a critical patch to all people as soon as possible. Resist it. A buggy patch may do more harm than the vulnerability it is patching. It is always best to roll out to a small pilot group first.
- Neglect of Third-Party Applications: A lot of companies patch Windows and ignore Adobe, Java, Chrome, etc. Hackers are aware of this and will often attack these applications. A holistic approach to patching is good.
- Deploying Outside of a Maintenance Window: Rebooting a user’s computer in the middle of a presentation is a sure fire way to make enemies. Make sure you have well defined maintenance windows (e.g. 2AM – 4AM) and inform your users.
- Set and Forget Mistake: Automation is great, but it is not magic. You have to continue to monitor your dashboard to see failed deployments, read reports and adjust your policies. Patch management is not a single project, but a continuing process.
Deployment Roadmap & Best Practices
You are prepared to operate your new best Enterprise Patch Management Software. Use this easy step-by-step plan:
1. Discover and inventory (1st week)
- Install the agent of the system in all endpoints.
- The best Enterprise Patch Management Software searches all machines and documents all hardware, each software title, and the patch status of each program. This scan is the beginning point.
2. Write policies and establish test groups (1 st -2 nd week):
- Patching policies design. As an example: “All critical security patches should be automatically approved and deployed on a Wednesday at 2 AM.” Or, Feature updates should be manually approved.
- Select a pilot group. Add machines of various departments such as a PC in the finance department, a Mac in the marketing department, a laptop in the sales department to ensure that the software is compatible with a broad range of machines.
3. Deployment and testing of pilots (3 rd week):
- Install best Enterprise Patch Management Software on the pilot group.
- Watch closely. Did all patches go through? Did any of the pilot group report problems? In case a patch creates problems, roll back.
4. Gradual implementation (4 th week and subsequent):
- Once the pilot is successful, roll-out in stages. Begin with IT and proceed to other tech-savvy teams and continue to roll out until the whole organization is reached. This easy deployment minimizes the effect in case of any untoward event.
5. Monitor, report and refine:
- The system has gone live. Keep track of the dashboard, review weekly success/failure reports and refine your policies with time.
- Happy safer, more stable IT environment!
Conclusion
Security is not a luxury, it is a necessity to survival. best Enterprise Patch Management Software is an intelligent investment that reduces risk and saves time. You can now do all that automatically instead of patching software by hand.
Automation reduces your attack surface, maintains your systems in good health and assists you to demonstrate compliance by printing a low-level report. Take the bull by its horns, install it and provide your business with a safe foundation.
FAQs
1. What is the distinction between an update and a patch?
A minor correction of a security problem or bug is known as a patch.
An update can include a number of patches or introduce new features and more significant changes.
In practice, the two terms are used interchangeably.
2. How frequently shall we patch our systems?
A non-critical update should be done on a regular basis (monthly or quarterly, e.g. a common model is so-called Patch Tuesday).
3. Is patch management a security thing?
No! Although security is the main motivating factor, patches also resolve performance bugs, resolve stability problems, and occasionally add new features, resulting in an improved user experience.
4. Are there free enterprise patch management tools I can use?
There are some free tools but they tend to not have the automation, wide third-party support, reporting, and centralized management that an enterprise requires. To a business, the potential cost of a missed patch is much higher than a professional solution.
 Get 50% off on Vault theme. Limited time offer!
Get 50% off on Vault theme. Limited time offer!